Imagine pouring your heart and creativity into building your brand or content, only to see someone else stealing your ideas and reaping the benefits.
Securing your intellectual property (IP) safeguards your hard work. Copyright and trademarks grant you legal ownership, allowing you to control how your work is used and distributed.
This protection empowers you in several ways. Firstly, it deters copycats and discourages others from imitating your brand or content. Secondly, it simplifies taking down infringing material. With registered IP, platforms are more inclined to remove stolen content, minimizing damage to your reputation and livelihood.
Finally, it can enhance your business value. Protected creations become assets, potentially increasing your worth for partnerships, licensing deals, or even a future sale.
What is a trademark?
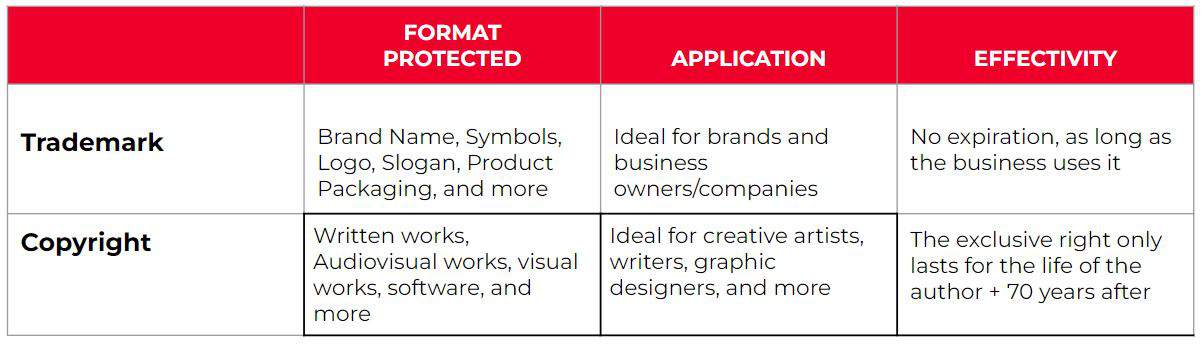
A trademark is a recognizable symbol, word, phrase or design that distinguishes a specific brand, product or service from others. This serves as a unique mark that sets you apart and can communicate your business identity alone.
This specific mark is also associated with a brand’s reputation and quality — to some extent, it can also be a brand’s business card.
It can also include specific choice of colors, elements and symbols that may be reflected in a business’ official product packaging, marketing materials, and more.
All in all, securing a trademark will be beneficial in terms of building and strengthening brand awareness for the long term.
Some of the trademark applications may include:
- Brand names – Name of your company, product, or service
- Logos – This is the visual symbol that embodies your brand identity
- Slogans – Usually a catchy phrase associated with your brand
- Product packaging – Design elements that are strategically put together to make your product stand out from the display
Examples of popular trademarks we love are:
- Apple’s iconic bitten apple logo
- Nike’s swoosh logo
- Mcdonald’s classic golden arches
- Netflix’s start-up audio
- Christian Louboutin’s show-stopping heels with red soles
These trademarks are deeply associated with the brand and even without any elements other than the mark, we still recognize it.

What is copyright?
Copyright, on the other hand, is intended to protect creative works and establish authorship. Securing this establishes an exclusive right for the owner to control the reproduction, distribution and adaptation of their works.
Copyright is intended for creative works including but not limited to the following:
- Written works – This includes books, articles, poems, and website content.
- Visual works – Paintings, drawings, photographs, sculptures, and graphic designs
- Audiovisual works – Movies, TV shows, audio, and melody
- Software – Computer programs, applications, and video games
Upon creation of work, copyright is immediately in place. You just need to provide proof of creation and authorship. However, to ensure even stronger legal protection against infringement, it will be better to apply straight to the copyright office.
Copyrighted works are often marked with the copyright symbol (©) followed by the year of creation and the copyright holder’s name.
Some copyright examples are the following:
- Taylor Swift and her masters – her right to re-record and distribute
- Disney and its characters, like Mickey Mouse – their right to create works of art in various formats with the character
- J.K. Rowling and Harry Potter franchise – her right to exclusive reproduce and allow adaptation

However, copyright protection doesn’t last forever. For works created after 1978, the exclusive right only lasts for the life of the author + 70 years after. After that, the creative works will be available in the public domain, open for use, adaptation and reproduction.
One example of this is Winnie-the-Pooh whose copyright was held exclusively by Disney for many years but recently became open for public use when its copyright expired in 2022.
Though this may mean bad news for Disney, what they did was secure the trademark separately.
Trademark vs copyright: key differences
Now that we’ve established what both trademark and copyright are, it’s time to set a table with their differences and what they are used for:
Protect your business, protect your intellectual property
A company or business can have both — trademark and copyright. Just make sure to apply for what is applicable to protect your rights as owner of a brand or author of creative works.
Securing your intellectual property is an investment in your business and creative future.
More helpful tips to build your brand online:
How to Build Your Brand through Vlogs
How to Manage Your Brand Reputation Online
How to Win Customers through Emotional Branding







